Low Cost Country Sourcing: Top Location Picks and Benefits
- Date:
- Author: SVI Content Team
- Share:
In the global supply chain, Low Cost Country Sourcing (LCCS) is a strategy where a company from high-cost countries (HCC) sources goods from low-cost countries (LCC) with less expensive labor and production costs.
To remain competitive in the market, most businesses are manufacturing products overseas to make their prices competitive and manage costs effectively. Inflation and tariffs push up manufacturing costs globally, making sources from low-cost countries necessary.
Where is your destination for manufacturing, and what can you benefit from it? In this blog, you will find the low cost country sourcing list and learn about the opportunities and challenges you may face.
Key Factors to Consider When Choosing the Best Cost Country
Though countries with lower cost do not mean you pick any one of the nations with the lowest costs, as manufacturing capabilities are also an important factor to evaluate. You will need to take lots of aspects into consideration to find a suitable location that works for your operation.
- Labor costs and availability
- manufacturing infrastructure
- supplier pool
- key industries
- quality regulations
- legal and regulatory framework
- trade agreements
- raw material availability
- shipping lead times
- ……
Part 1: List of Top Low Cost Manufacturing Countries
1. China
China is always on the list, whether as a primary option or alternative. It offers a well-established production ecosystem that balances competitive pricing with reliable quality and volume. And its mature infrastructure is equipped to handle a vast range of products, making it a resilient choice for many importers.
From the perspective of the U.S. imports last year, China was the second-largest source of U.S. imports. You can see how strong the manufacturing capacity is.
Key industries:
According to the top exports from China in 2024, its strengths lie in electronics, machinery, automotive parts, plastics, furniture, and textiles.
- Electrical machinery, equipment
- Machinery including computers
- Vehicles
- Plastics, plastic articles
- Furniture, bedding, lighting, signs, prefab buildings
Avg. Monthly Minimum Wage:
The minimum wages are set by each province or city. As of July 2025, most major provinces and cities have minimum wages between RMB 1,700 and RMB 2,740 (about US$236-$381).
Most Manufacturing Cities in China
- Shenzhen: RMB 2,520/month (as of Apr 2025)
- Guangzhou: RMB 2,500/month (as of Apr 2025)
- Dongguan: RMB 2,080/month (as of Apr 2025)
- Suzhou: RMB 2,490/month (as of Jan 2024)
- Hangzhou: RMB 2,490/month (as of Jan 2024)
- Ningbo: RMB 2,490/month (as of Jan 2024)
- Yiwu: RMB 2,260/month (as of Jan 2024)
- Changsha: RMB 2,100/month (as of Sep 2024)
- Qingdao: RMB 2,200/month (as of Oct 2023)
- Chengdu: RMB 2,330/month (as of Jan 2025)
- Wuhan: RMB 2,210/month (as of Feb 2024)
2. Vietnam
Vietnam is one of the most potential manufacturing hubs in Southeast Asia. It ranked as the 8th largest trading partner of the United States in 2024, and remains the top “China +1” alternative.
Its strategic location adjacent to China, along with its growing trade agreements and manufacturing expertise, has made it a rising star.
Key industries:
Based on the exports of Vietnam from 2024, the leading exports of Vietnam were strong in textiles, electronics, footwear and furniture.
- Electrical machinery, equipment
- Machinery including computers
- Footwear
- Textile and apparel
- Furniture, bedding, lighting, signs, prefab buildings
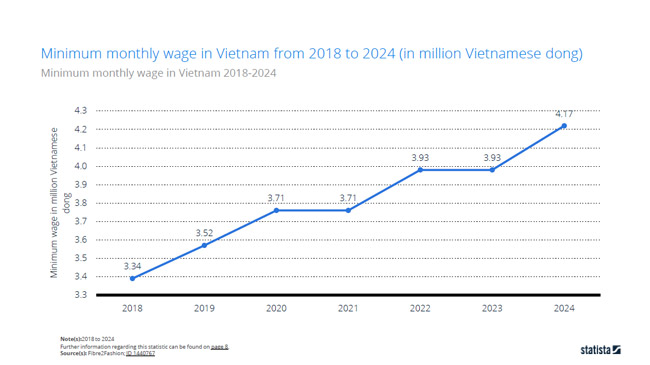
Avg. Monthly Minimum Wage:
Vietnam’s minimum wage is divided into different regions, and the average is about VND 4,170,000/month. The structure is divided into four regions:
- Region I (major cities/industrial hubs): VND 4,960,000/month (US$190)
- Region II (moderate development): VND 4,410,000/month (US$170)
- Region III (developing areas): VND 3,860,000/month (US$148)
- Region IV (rural/mountainous): VND 3,450,000/month (US$132)
3. Mexico
Mexico is a strategic option for U.S. importers due to its proximity and benefits under the United States-Mexico-Canada Agreement (USMCA). It was the top trading partner with the U.S. in 2024.
While labor costs are higher than in many Asian countries, Mexico is the preferred nearshore destination for companies that prioritize faster lead times and reduced shipping costs.
Key industries:
Automotive, electronics and machinery are Mexico’s best performers in the 2024 exports.
- Vehicles
- Machinery including computers
- Electrical machinery, equipment
- Optical, technical, medical apparatus
- Mineral fuels including oil
Avg. Monthly Minimum Wage:
Mexico sets its minimum wage by day, not by month, and adjusts rates by region. The two main rates in 2025 are:
- 2025 General: MXN 278.80 per day (US$15), totaling about MXN 8,364/month (US$452).
- 2025 Northern Border Free Zone: MXN 419.88 per day (US$22.65), totaling about MXN 12,596/month (US$680).
Compared to last year, the monthly payment has increased by 12% in 2025.
- 2024 General: MXN 248.93 per day, totaling about MXN 7,468/month (US$440).
- 2024 Northern Border Free Zone: MXN 374.89 per day, totaling about MXN 11,246/month (US$662).
4. Indonesia
Indonesia offers competitive product pricing and access to a large domestic market. Its rich raw material resources support its growth as a rising manufacturing base.
Key industries:
The data reports from 2024 to 2025 show that electronics, vehicles and footwear are its key exports, in addition to its strong natural resource exports.
- Mineral fuels
- Animal/vegetable fats and oils
- Iron and steel
- Electrical machinery and equipment
- Vehicles
Avg. Monthly Minimum Wage:
Indonesia’s minimum wage in 2025 is highly regionalized, with most workers earning between IDR 2.1 million and 5.4 million per month (about US$130–$332).
- Jakarta – IDR 5,396,760/month
- Aceh – IDR 3,685,615/month
- West Java – IDR 2,191,232/month
- West Sulawesi – IDR 2,104,430/month
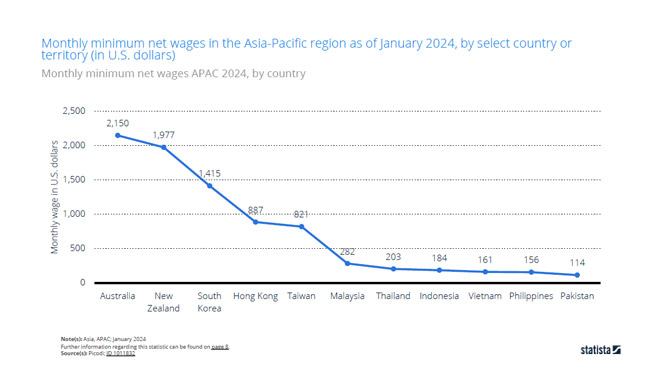
And according to Statista, the monthly minimum net wage in Indonesia is about $184 as of Jan 2024.
5. Thailand
Besides its tourism, Thailand has a well-developed infrastructure and a strong focus on specific industrial sectors like automotive. It benefits from the Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership (RCEP) with countries across the Asia-Pacific region. And its largest export markets are United States, China, and Japan.
Key industries:
Electronics and machinery, automotive are Thailand’s top exports according to data from Trading Economics in 2024.
- Electrical machinery, equipment
- Machinery including computers
- Vehicles
- Rubbers, rubber articles
- Gems, precious metals
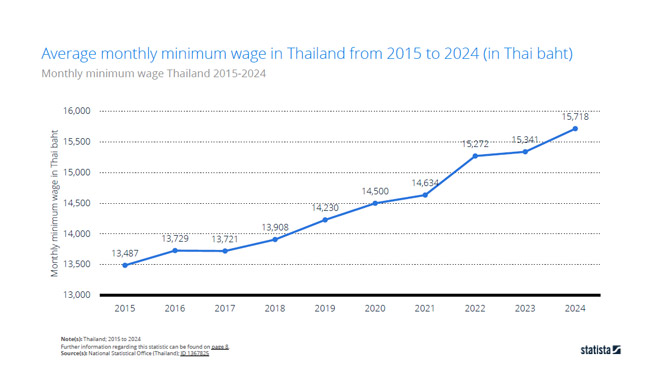
Avg. Monthly Minimum Wage:
The minimum wage in Thailand sets the standard for a day. As of Jan 2025, the minimum daily wage in areas varies and ranges from:
- THB 400/day (US$12.3)
- THB 380/day (US$11.7)
- THB 372/day (US$11.5)
- THB 337/day (US$10.4)
According to Statista, we can know that the 2024 average minimum monthly wage in Thailand is about THB 15,178/month (about US$468).
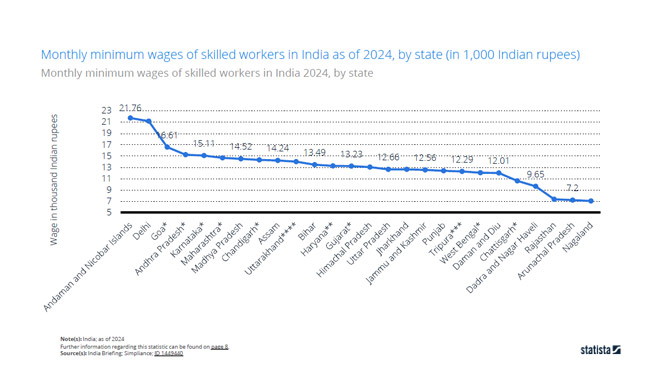
6. India
As the most populous country in the world, India, offers a vast and growing workforce. Strategically located in the Indo-Asia-Pacific region and in proximity to China, it stands out as one of the best-value sourcing destinations.
Key industries:
- Refined petroleum products
- Pharmaceuticals
- Gems and jewellery
- Automobiles
- Textiles and garments
Avg. Monthly Minimum Wage:
Each state in India sets its own monthly minimum wage, and the salary varies by skill level: unskilled, semi-skilled, skilled, and highly skilled.
While the official national floor wage ranges from INR 5,340 to 5,616/month (US$65 to $68), the actual minimums in most large states and cities are much higher, typically between INR 17,000 to 25,000 /month (US$196 to $289).
7. Bangladesh
Bangladesh is one of the most cost-effective markets for textile and apparel manufacturing. The low labor cost and high-volume apparel output make it a preferred choice for clothing companies.
Key industries:
Garments are the major exports in Bangladesh, accounting for nearly half of the country’s total export value.
- Readymade Garments
- Jute and Jute Products
- Footwear
- Miscellaneous textiles
- Headgear and Caps
Avg. Monthly Minimum Wage:
The average statutory monthly minimum wage in Bangladesh in 2025 is BDT 12,500 (about US$104). The rate primarily applies to the ready-made garment sector and most formal sectors across the country.
Part 2: Benefits of Low Cost Country Sourcing
1. Lower Production and Operational Costs
Countries chosen to be the low-cost manufacturing destination typically possess affordable costs in various aspects: labor, operations, raw materials, and overhead. Importers from high-cost countries can take advantage of the cheaper costs to optimize their profit margins.
2. Get a Competitive Edge on Pricing
One major advantage of low-cost country sourcing is the ability to offer more competitive product prices in the market. Lower unit costs give brands pricing flexibility, which helps them stay competitive while protecting or improving profit margins.
3. Reduce Risks of Relying on a Single Source
In addition to cost savings, placing your sources across multiple low-cost regions helps companies spread risk. Diversifying production builds a stronger, more resilient supply chain. This approach can lower the risk of disruptions tied to political or environmental events, especially useful in today’s unpredictable global environment.
4. Take Advantage of Trade Agreements
Many low-cost manufacturing countries have established trade agreements with big trading nations such as the U.S. and China. Businesses can capitalize on these agreements to lower import duties, shorten customs clearance times, and improve overall cost efficiency.
Though the outlook for tariffs is uncertain, it is still promising to build your supplier network in countries with favorable trade deals in the long run.
Part 3: Risks of Low Cost Country Sourcing
1. Product Quality Control Challenges
Quality control is a big issue to maintain while sourcing your products from low-cost countries.
Quality issues can be caused by many reasons, such as inconsistent QC measures, various standards, human errors, etc. Factories that hold different quality standards or lack familiarity with international regulations could lead to product defects. This may cause you more budget for testing and inspection for the rework.
2. Currency Fluctuations
International trade is vulnerable to fluctuating exchange rates and inflation. Currency volatility can significantly affect your landed cost. When the currency of your sourcing country weakens, it may offer a cost advantage, but sudden appreciation can hurt your margins.
In this situation, companies must monitor currency trends and, when possible, negotiate pricing strategies that account for this risk.
3. Longer Lead Times, Communication & Cultural Differences
Managing a supply chain across continents introduces complexities like longer shipping times, different time zones, and potential language barriers.
These factors can slow down your time-to-market and require more sophisticated logistics planning.
4. Exposure to Supply Chain Disruptions
The global supply chain, characterized by its reliance on multiple countries and extensive shipping distances, is highly vulnerable to disruptions. These can range from natural disasters and geopolitical policy changes to trade tariffs.
Each link in the supply chain should be prepared for the risks and make a plan to confront all the changes.
5. Ethical and Sustainability Concerns
The practices of your suppliers are directly related to your brand’s reputation. Some regions may have less stringent laws regarding ethical labor practices and environmental sustainability.
It is crucial to avoid engagement with factories that exhibit unethical practices, such as child labor, substandard working conditions, or environmental pollution.
Part 4: Tips for Best Value Country Sourcing
⭕ Analyze the country’s overall fit, like duties and capabilities
Look beyond labor costs. Start screening countries by evaluating top factors like tariff structures and industrial capabilities. Then consider political stability, economic conditions, logistics infrastructure, and cultural compatibility.
⭕ Always calculate the total cost before committing
The cheapest option isn’t always the best; focus on “best value” by calculating the total landed cost. This includes not just the unit price but also shipping, tariffs, the cost of quality assurance, and possible delays.
⭕ Make a pre-qualification checklist and conduct a factory audit
Before engaging a factory, thoroughly verify certifications, export experience, production capacity, and financial health.
⭕ Vet suppliers closely for compliance and ethical standards
Ensure suppliers meet labor, environmental, and safety standards to protect your brand and avoid reputational risks.
⭕ Start with trial orders and third-party inspections and testing
Run small test orders to validate quality, responsiveness, and delivery reliability. Use third-party inspectors for objective checks and lab testing where needed.
⭕ Consult with legal and trade experts to stay compliant and protect IP
Engage local legal advisors or trade consultants to understand regulations, IP protection, and contract laws in your sourcing country.
⭕ Know when to work with a sourcing agent
A local sourcing partner can bridge language and cultural gaps, manage factory visits, and ensure smoother negotiations. It is helpful if you’re new to a region.
⭕ Diversify your sourcing countries
Don’t rely on just one country. Spread production across 2 to 3 regions to reduce exposure to supply shocks, currency swings, policy shifts, and tariffs.
Conclusion
Companies from high-cost countries can leverage the low cost country sourcing advantages from lower production costs, improved pricing competitiveness, to diversified supply chains. But the process also comes with real risks. The important thing is that you don’t chase price alone.
Successful importers focus on value, which includes quality, reliability, and long-term resilience. If you need support navigating this process, SVI Global is here for you.
With over 20 years of experience in top value markets like China, Vietnam, Mexico, Indonesia, and more, we assist you in finding the right suppliers by leveraging our deep supplier networks and a strong focus on quality control and compliance.