A Step-by-Step Guide: How to Calculate Total Manufacturing Costs
- Date:
- Author: SVI Content Team
- Share:
Want to know if you have received fair prices from factories and become more competitive in the business market? Producing items involves many activities to ensure the success of a production.
Understanding how to calculate total manufacturing cost is essential. It is not just about knowing how much it costs to make a product; it’s about grasping the nitty-gritty details of those costs and their impact on the overall profitability of the business.
In this blog, you can explore what is involved in manufacturing costs and follow the steps to calculate total manufacturing costs with formulas.
Get ready and pack your bag for the upcoming feast of knowledge.
Part 1. What Is Manufacturing Cost?
1) What Does It Mean
In a nutshell, manufacturing costs are all expenses incurred in the process of manufacturing a product. It shows how much it costs for the whole production, and it usually covers costs in material, labor, and manufacturing overhead.
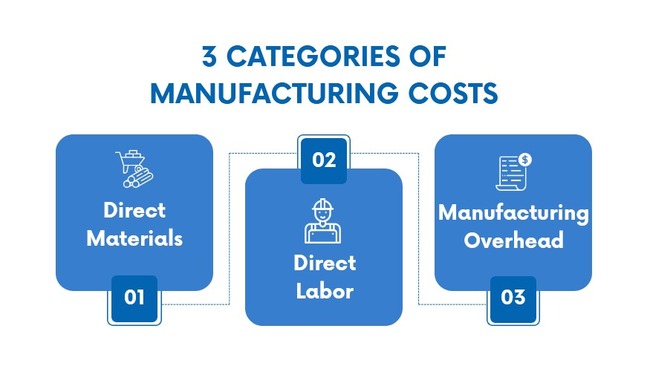
2) What Is Included in the Manufacturing Cost
These costs encompass all the resources and inputs used in manufacturing.
✅ Direct Materials
The costs are the expenses associated with raw materials that are directly used as a part of the final products during manufacturing.
They are direct manufacturing costs and can be traced to specific units of products being made. These costs vary directly with the production volume.
Examples: wood, nails, and fabric for furniture, coffee beans and cups for coffee
✅ Direct Labor
This refers to the wages, benefits, or payroll taxes paid to workers directly engaged in the manufacturing process, like assembly line workers, not factory supervisors.
These expenses are associated with the production of goods and can be easily traced to specific units of output.
Examples: machine operators, assembly line workers, quality inspectors
✅ Manufacturing Overhead
These are indirect manufacturing costs associated with production that cannot be easily traced to specific units of output.
They support the production process as a whole rather than directly contributing to the production of individual units, such as indirect labor costs and material costs.
Examples: Property taxes, energy costs, utilities, factory rent, equipment depreciation, and salaries of personnel in management
Part 2. How to Calculate Total Manufacturing Costs – Step by Step
📌 Total Manufacturing Cost Formula
To compute the manufacturing costs in your production, you will need to sum up the costs of direct materials, direct labor, and manufacturing overhead.
Here is the total manufacturing cost formula:
Total Manufacturing Costs = Direct Materials + Direct Labor + Manufacturing Overhead
While the formula is simple, how do you determine the precise amount for each type of manufacturing cost? Let’s break it down.
1. Direct Materials Cost Formula
If the manufacturer has stock for the materials used in production, calculate the value of the existing inventory.
Next, add the cost of newly purchased raw materials this time.
At last, check out how many raw materials are left after production and subtract their value.
Follow this simple formula to calculate the cost of direct materials used:
Total Direct Material Cost = Beginning Materials Inventory + Materials Purchased – Ending Materials Inventory
📒 Example:
For a stationery factory, this could include paper, ink, and plastic covers for notebooks or pens.
- Beginning materials inventory: $10,000
- Materials purchased: $20,000
- Ending materials inventory: $5,000
Then, the total direct material cost = $10,000 + $20,000 – $5,000 = $25,000
2. Direct Labor Cost Formula
To determine direct labor cost, you will need to sum up all wages, payroll, and benefits of employees who worked directly for the production in a certain period.
For more accurate hours worked:
Total Direct Labor Cost = Direct Labor Hourly Rate × Total Direct Labor Hours
Where:
- Direct Labor Hourly Rate = wages, taxes, benefits / total labor hours worked
- Total Direct Labor Hours = sum of hours worked by direct staff in the period
📍 Direct Labor Cost Per Unit
While the total cost is good for overall budgeting, the direct labor cost per unit is the most valuable metric for strategic business decisions.
It tells you the exact labor cost embedded in each individual product you make, and you can set a profitable selling price based on it.
How to calculate direct labor cost per unit:
The formula is:
- Using hourly rate:
Direct Labor Cost Per Unit = Direct Labor Hourly Rate × Total Direct Labor Hours per Unit
- Using Totals:
Direct Labor Cost per Unit = Total Direct Labor Cost / Total Units Produced
📒 Example:
Given (monthly period):
- Wages paid to line staff: $40,000
- Payroll taxes & benefits: $5,500
- Overtime and bonuses: $1,000
- Temp staff fees: $500
- Total direct labor hours worked in a month = 3,500 hours
- Total Produced notebook units: 8750 units
- Labor time to make one notebook = 0.40 hours
Option 1 (All add up):
Total Direct Labor Cost = $40,000 + 5,500 + 1,000 + 500 = $47,000
Direct Labor Cost per Unit = $47,000 / 8750 = $5.37 / unit
Option 2 (Based on hours):
Direct Labor Hourly Rate = $47,000 ÷ 3,500 = $13.43 / hour
Total Direct Labor Cost = $13.43 × 3,500 = $47,000
Total Direct Labor Hours per Unit = 3,500 ÷ 8,750 = 0.4 hours
Direct Labor Cost Per Unit = $13.43 × 0.4 = $5.37 / unit
3. Manufacturing Overhead Cost Formula
As you know from the previous definition, manufacturing overhead costs are everything except direct labor and direct material costs. Add all indirect costs and you can use the following formula to learn how to calculate manufacturing overhead cost:
Manufacturing Overhead Cost = Sum of Indirect Costs
📒 Example:
Indirect costs include:
- Factory rent: $8,000/month
- Utilities: $5,000/month
- Supervisor salaries: $5,000/month
- Equipment depreciation: $12,000/year
- Maintenance expenses: $10,800/year
According to the formula:
Total manufacturing overhead cost
= $8,000 + $5,000 + $5,000 + $12,000/12 + $10,8800/12
= $8,000 + $5,000 + $5,000 + $1,000 + $900 = $19,900 per month
By following these formulas and examples, you’ll learn how to compute total manufacturing cost. This will help you have a clear overview of your spending and optimize your production processes for maximum profitability.
If you prefer a more streamlined method, SVI Global suggests engaging in open discussions with factories. During these conversations, you can kindly request cost breakdowns that include detailed calculation formulas. This approach allows companies to verify and evaluate pricing accurately, fostering transparency between both parties. It simplifies the cost calculation process and strengthens trust and collaboration between companies and suppliers.
Need Help for Your Sourcing Project?
Let SVI Global find the right suppliers and manage your project.
We guarantee quality and on-time delivery!
FAQ about Manufacturing Costs
Q1. What are the main factors affecting manufacturing costs?
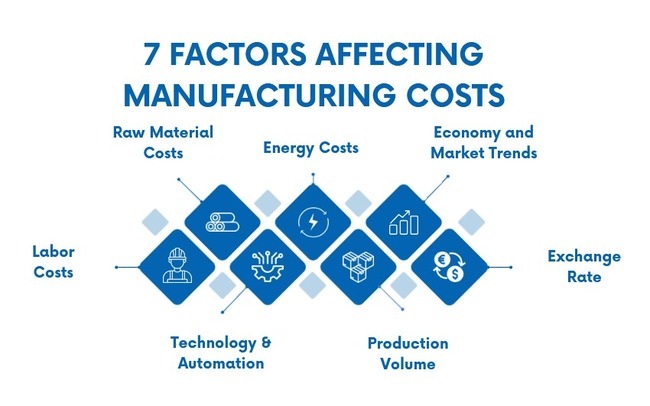
If a company is to be profitable, it is vital to conduct a comprehensive cost breakdown that includes every aspect of production. Here are some variable key factors to consider:
- Labor Costs: Wages, benefits, and labor regulations directly shape efficiency and productivity. Some businesses reduce costs by outsourcing manufacturing to countries with lower wages.
- Raw Material Costs: Prices for metals, plastics, paper, or chemicals fluctuate with supply and demand, geopolitical events, and global market trends.
- Technology and Automation: While automation requires upfront investment, it cuts labor costs, reduces lead times, and improves long-term efficiency.
- Energy Costs: Manufacturing often requires high energy use. Oil prices, government policies, and renewable energy developments all impact expenses.
- Production Volume: Larger orders lower per-unit costs due to economies of scale, while small runs push costs higher.
- Economic Conditions: Shifts in consumer demand, market trends, or recessions can affect production volumes and overall costs.
- Exchange Rates: For global supply chains, currency fluctuations can increase or reduce the final manufacturing cost.
Q2. Why do you need to calculate manufacturing cost?
Understanding how to calculate manufacturing cost is critical for businesses to get a clear picture of the product cost. It helps businesses:
- Set accurate prices that cover expenses and generate profit.
- Control costs by spotting inefficiencies and tracking budget variances.
- Improve efficiency through waste reduction and smarter resource use.
- Build accurate Bills of Materials (BOMs) for better production planning and inventory control.
- Negotiate with suppliers using a clear breakdown of real costs.
The Bottom Line
Manufacturing costs can impact various aspects of a business. It will not merely shape pricing and profitability, but will also affect supplier relationships, market competitiveness, and more. Understanding how to calculate manufacturing cost is important for achieving long-term success and sustainability.
This blog has provided you with its definition and the formulas for direct materials, direct labor, and manufacturing overhead costs. Companies with this knowledge can make informed decisions regarding pricing strategies, budgeting, and resource allocation.
However, seeking a better price from suppliers for overseas sourcing can be a challenge. This is where SVI Global, a leading supply chain solution provider, can offer invaluable assistance. With our expertise in supply chain management, SVI Global can help businesses negotiate competitive prices with suppliers, optimize procurement processes, and streamline supply chain operations. Our support will enable organizations to turn challenges into opportunities, achieve cost savings and enhance their competitive advantage in the marketplace.
Our professional services cover multiple aspects of the supply chain. Further information can be obtained by consulting with us.